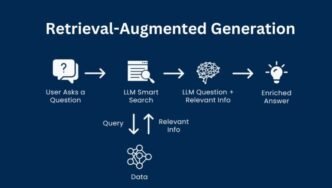
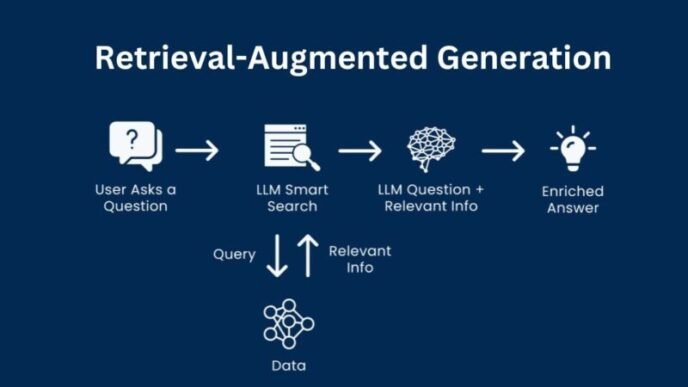
Computer vision is a fascinating domain within artificial intelligence that equips machines with the capacity to interpret and understand the visual world. By mimicking human vision, computer vision systems can identify objects, faces, scenes, and activities in images and videos. This capability transforms how machines interact with their environments, making them smarter, more effective, and capable of undertaking complex tasks independently.
Understanding the Basics of Computer Vision
The Essence of Computer Vision
Computer vision strives to replicate human visual perception using software and hardware. This field involves capturing, processing, analyzing, and understanding digital images or videos to automate tasks traditionally done by human sight. Innovations in this area are critical for advancements in autonomous vehicles, quality control systems, healthcare imaging, and more.
For an introduction to the fundamentals of computer vision, click here.
How Computer Vision Works
At its core, computer vision uses digital images from cameras and sensors, as well as deep learning models, to identify patterns and make sense of what is being seen. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
1. Image Acquisition: This is the process of capturing live or static visual information, typically using digital cameras, videos, or 3D sensors.
2. Pre-processing: Enhancing image data (scaling, de-noising, etc.) to improve the accuracy of the analysis.
3. Feature Extraction: Identifying important parts of the image data that are useful for detecting objects or descriptions.
4. Detection/Segmentation: Separating objects within images and classifying them.
5. High-Level Processing: Making sense of an ensemble of recognized objects, often involving complex AI algorithms.
6. Decision Making: Taking action based on the interpretation of the visual data.
Key Technologies Behind Computer Vision
Machine Learning and Neural Networks
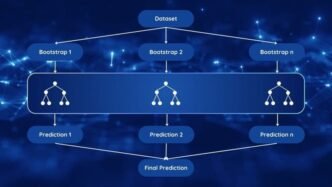
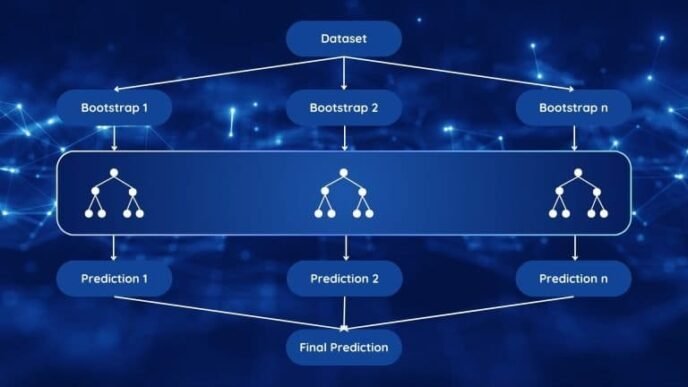
Machine learning, particularly deep learning with neural networks, plays a vital role in computer vision. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a type of deep learning model, are especially pivotal. These networks are proficient at analyzing visual imagery and are structured similarly to the human brain’s connectivity, focusing on recognizing spatial hierarchies in images.
To dive deeper into CNNs and their application in computer vision, visit this detailed guide.
Edge Detection and Pattern Recognition
Edge detection helps delineate the boundaries of objects within images, which is crucial for object and scene analysis. Pattern recognition allows systems to categorize and label the data they see, based on learned patterns from training datasets.
Image Processing Techniques
Various image processing techniques, such as filtering, texture analysis, geometric transformations, and color analysis, are used to improve image quality and extraction features that contribute to the overall understanding of the image.
Applications of Computer Vision
Automotive Industry: Autonomous Driving
Computer vision is pivotal in developing autonomous vehicles. It enables cars to recognize obstacles, interpret traffic signs, and navigate safely through environments without human intervention.
Healthcare: Medical Imaging and Diagnosis
In healthcare, computer vision techniques enhance medical imaging tools like MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays. These tools assist doctors in diagnosing diseases with higher accuracy and in conducting intricate surgeries.
Retail and Surveillance: Security and Customer Insights
Retail stores and security systems use computer vision to monitor spaces for unusual activities, track customer traffic, and analyze consumer behavior patterns.
Agriculture: Crop Monitoring and Management
Advanced computer vision algorithms are employed in agriculture to monitor crop health, predict yields, and detect weed or pest infestations.
Manufacturing: Quality Control
In manufacturing, computer vision systems ensure the quality of products by detecting defects and ensuring that assembly lines function smoothly.
For more on the expansive applications of computer vision, explore this comprehensive overview.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Privacy Concerns
The widespread use of computer vision in surveillance and data collection raises significant privacy issues, prompting calls for regulations to protect individual privacy rights.
Bias in AI Models
Bias in training data can lead computer vision systems to develop biased, unfair, or incorrect interpretations. Addressing these biases is crucial for equitable and accurate system outcomes.
Computational Requirements
The high computational demand of processing large volumes of visual data in real-time continues to challenge current hardware capabilities, driving ongoing advancements in computing technologies.
The Future of Computer Vision
The potential of computer vision is vast and still largely untapped. As technology advances, we can expect broader applications, from more sophisticated robot interactions to smarter city infrastructures and beyond. The integration of augmented reality and computer vision is particularly promising, offering even more immersive and interactive technological experiences.
For future trends and predictions in computer vision, consider reading this forecast by Gartner.
Conclusion
Computer vision is revolutionizing the way machines interact with the world. By giving machines the ability to see, understand, and respond to visual inputs, this technology is creating smarter, more autonomous systems that enhance human capabilities and efficiencies across numerous sectors. As we continue to explore and expand the boundaries of what computer vision can achieve, its impact on daily life and global industries is set to grow exponentially.